Getting Started
Automatically Generate ERD of Your Django Models
Create django project
django-admin startproject mysite
This will create the bellow files and directories.
mysite/
manage.py
mysite/
__init__.py
settings.py
urls.py
asgi.py
wsgi.py
Create a blog application
python manage.py startapp blog
This will create the bellow folders and files.
mysite/
....
....
blog/
migrations/
__init__.py
__init__.py
admin.py
apps.py
models.py
tests.py
views.py
Create a virtual environment and install Django
# Create virtual environment
virtualenv .venv
# Activate the virtual environment
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install Django
pip install Django
Create database models
Let’s create the database structure of our blog application
blog/models.py
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.db import models
class Category(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=200)
slug = models.CharField(max_length=200)
description = models.CharField(max_length=350)
updated = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
created = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
class Article(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
categories = models.ManyToManyField(Category, related_name="categories")
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
slug = models.CharField(max_length=200)
title = models.CharField(max_length=300)
content = models.TextField()
updated = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
created = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
Register the blog application
mysite/settings.py
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
# project apps
'blog'
]
Run the project and migrate the models
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserver
If everything is fine you will get the bellow output.
❯ python manage.py runserver
Watching for file changes with StatReloader
Performing system checks...
System check identified no issues (0 silenced).
July 10, 2023 - 09:07:19
Django version 4.2.3, using settings 'mysite.settings'
Starting development server at http://127.0.0.1:8000/
Quit the server with CONTROL-C.
Install django-extensions package
Django Extensions is a collection of custom extensions for the Django Framework.
These include management commands, additional database fields, admin extensions and much more.
pip install django-extensions
# Install pydotplus for graph generation
pip install pydotplus
Setup the package
INSTALLED_APPS = [
"django.contrib.admin",
"django.contrib.auth",
"django.contrib.contenttypes",
"django.contrib.sessions",
"django.contrib.messages",
"django.contrib.staticfiles",
# installed apps
"django_extensions",
# project apps
"blog",
]
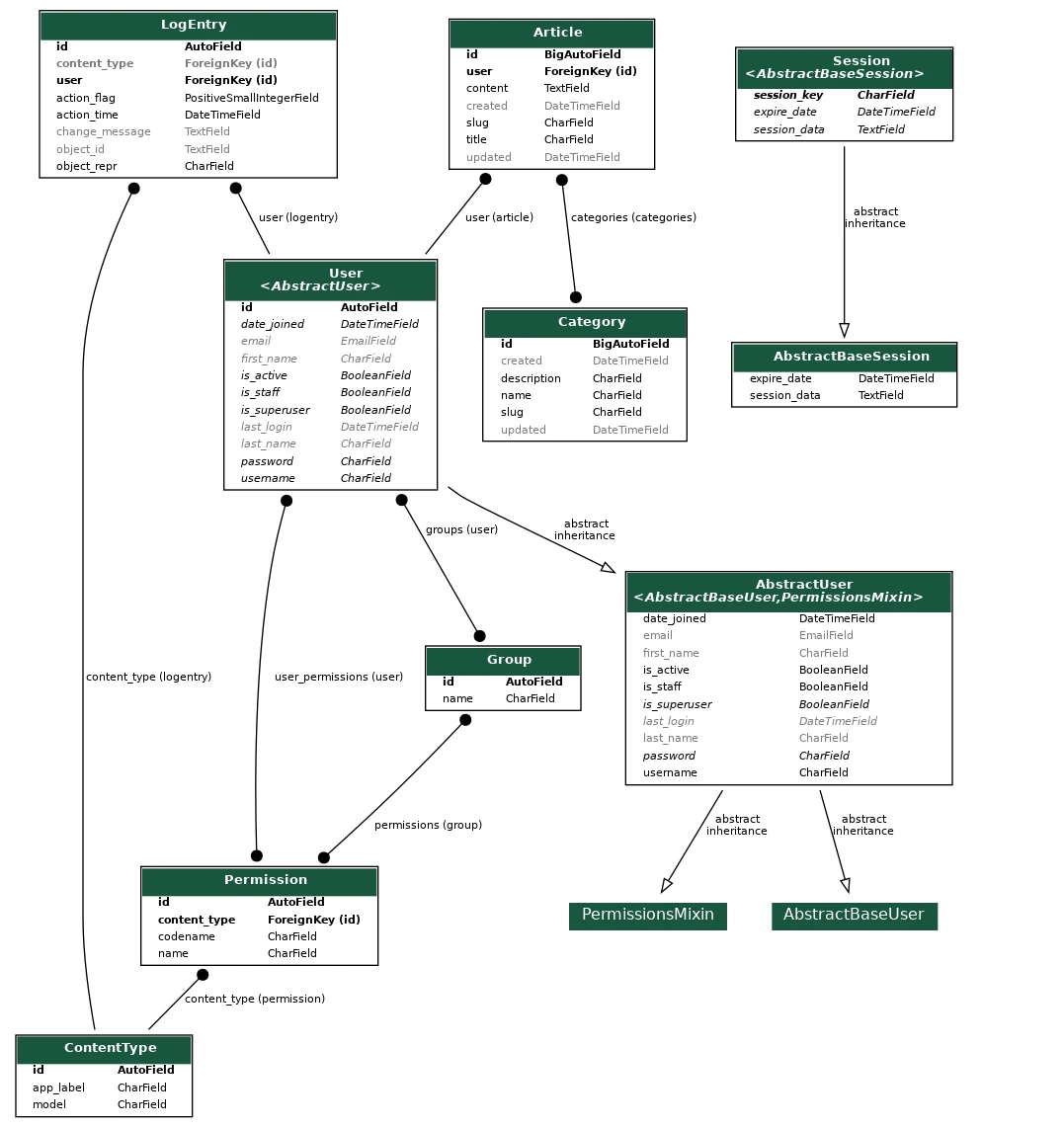
Generate the ERD
Generate ERD of all your project Models
# Generate ERD of all your DB tables
python manage.py graph_models -a -o myapp_models.png
Generate ERD of specific apps
# Generate ERD of specific apps
# python manage.py graph_models <app_name_1> <app_name_2> -o myapp_models.png
python manage.py graph_models blog auth -o myapp_models.png
-webp.webp)
Bonus django-extensions commands
Other usefull commands of django-extensions package.
❯ pm show_urls # List all you app urls
❯ python manage.py shell_plus
❯ python manage.py shell_plus --print-sql
❯ python manage.py list_signals
❯ python manage.py reset_db # Reset your database and prepare it for new migration
Generate admin panel Classes
# python manage.py admin_generator <your_app_name>
❯ python manage.py admin_generator blog
Generated Admin Classes
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Category, Article
@admin.register(Category)
class CategoryAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = (
'id',
'name',
'slug',
'description',
'updated',
'created',
)
list_filter = ('updated', 'created')
search_fields = ('name', 'slug')
prepopulated_fields = {'slug': ['name']}
@admin.register(Article)
class ArticleAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = (
'id',
'user',
'slug',
'title',
'content',
'updated',
'created',
)
list_filter = ('user', 'updated', 'created')
raw_id_fields = ('categories',)
search_fields = ('slug',)
Display a model’s info
# python manage.py list_model_info --model <app_name.Model>
❯ python manage.py list_model_info --model blog.Article
: '
blog.Article
Fields:
id -
user -
slug -
title -
content -
updated -
created -
categories -
Methods (non-private/internal):
adelete()
arefresh_from_db()
asave()
get_constraints()
get_next_by_created()
get_next_by_updated()
get_previous_by_created()
get_previous_by_updated()
validate_constraints()
Total Models Listed: 1
'

